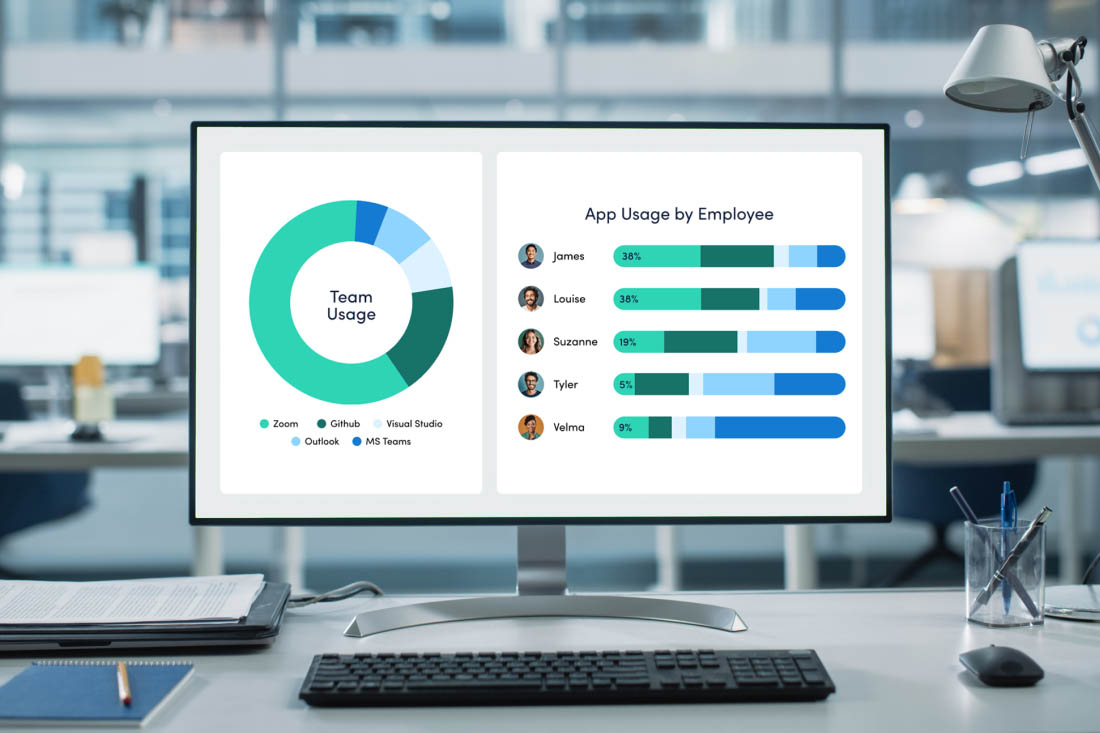
Measuring work productivity is an important part of running a successful business, especially in an era of remote work. Productivity is the benchmark for setting goals, identifying where to improve, and making financial decisions for the business. Follow ActivTrak’s step-by-step guide to find out how to measure employee productivity and optimize performance.
How to Measure Work Productivity in 8 Steps
Step 1: Define work productivity
The first step in measuring work productivity is defining what it means for your organization. Productivity measures the output or performance relative to the effort put in. A simplified equation to calculate productivity would be:
Employee Productivity = Total Output/Total Input
What “input” and “output” mean depend on your company’s business, industry and processes. Generally, most organizations will look at the quantity, quality and timeliness of tasks completed by an employee across a given period of time. But you may also use a comparison of the total time spent on each task to the corresponding output as a measurement of productivity.
Common ways you can measure productivity include:
- Per individual employee
- By team
- By the organization as a whole
- By project or output type
- By process
Employers need to track the time and resources used to complete tasks in order to identify areas where processes and systems should be better. This improves productivity, either by producing a higher number of units or completed projects, or the same number but at a higher quality.
Every organization needs to consider how to define productivity based on its specific processes, outputs and overall goals.
Step 2: Identify key performance indicators
The next step in measuring work productivity is to identify key performance indicators (KPIs). KPIs are specific metrics used to track and measure performance. These can include tasks completed, accuracy of work, quality of work and timeliness of tasks. KPIs will vary from company to company depending on what specific goals need to be achieved.
You need to make sure your KPIs are relevant to the job role and they’re actually measurable. They also have to be realistic and achievable. Finally, you’ll need to review KPIs regularly to make sure that they still make sense for your organization over time.
Once you’ve identified KPIs, you have to communicate them to the employee or employees so they’re aware of expectations and how their performance will be measured. Over time, employees will also need feedback on their performance against the KPIs so they can see their progress and be motivated to improve where necessary.
Step 3: Assess employee output
Once you’ve identified KPIs for employee roles, you can assess employee output. To do this, collect data on how an employee performs over a period of time (a month, a quarter or a year) and analyze it against KPIs to see what’s working and what isn’t. You should be able to see employee productivity based on individual performance and on a collective level, as well as which KPIs are unrealistic.
Assessing employee output isn’t just about collecting and analyzing data. It’s also about giving employees feedback on their performance and helping them identify areas for improvement. Regular performance reviews, one-on-one meetings and informal conversations all help employees understand their performance. This is an important part of keeping employees motivated to reach their goals.
Step 4: Measure task completion time
Measuring the amount of time it takes for employees to complete tasks is an important part of measuring productivity. This involves tracking time spent on each task or finding an average amount of time spent on completing tasks.
Accuracy is key to tracking completion time and levels of productivity. It may seem like a straightforward question, but to get a true view of how much time it takes to complete a task, you need to know more than just the number of hours worked. While it’s possible to simply track time using a timer or a stopwatch, task-tracking software (like ActivTrak) can provide a much more accurate and nuanced view of how long it takes individuals or teams to complete tasks.
Step 5: Track output quality and accuracy
A true measure of employee productivity includes the accuracy of output and quality. For example, measuring output against specifications or counting how often employees make mistakes.
Output quality can be a little tricky to analyze unless you have specific standards you can judge against. Some goods and services may be more difficult to measure quality for, so it’s important for each organization to define what a quality output looks like and communicate those standards. Everyone understanding how it’s measured is key to success.
One way to accurately measure quality is through customer satisfaction. Products or services that aren’t up to customer standards can lead to a decline in customer loyalty and a decrease in overall profits. Tracking output quality helps deliver offerings of a high standard to keep customers satisfied, and tracking quality can also be a window into employee morale.
If employees aren’t feeling motivated or feel undervalued, they may be less productive or more prone to making mistakes. Tracking this information can help you get employees the resources and support they need to feel their work is valued or their work-life balance is in sync with their needs.
Step 6: Establish benchmarks for productivity
In order to accurately measure progress over time and identify areas of improvement, you need to establish specific benchmarks for productivity. These can be based on several metrics, including:
- Past performance
- Industry standards
- Internal business targets
Your organization’s benchmarks are specific to your goals. For instance, if your goal is to increase sales, you’ll set benchmarks that reflect how much you want to increase sales. You’ll also need to consider available resources, such as how many employees you have, how much time they have, and what your budget is. Keeping these in mind will help you set benchmarks that are both realistic and achievable.
Once you’ve established benchmarks, you need to track progress against them and be prepared to make updates as needed. This means one of your benchmarks will be to regularly review data and adjust other benchmarks. You’ll also need to create processes to ensure you’re giving employees regular feedback on their performance and rewarding them for meeting or exceeding benchmarks.
Step 7: Determine the sources of productivity loss
Any organization will encounter situations where productivity is negatively impacted, and you’ll have to account for these in your measurements. Some factors that contribute to lower productivity include:
- Inefficient production processes
- Inadequate training
- Poor communication
Measuring the factors that detract from productivity can help you identify changes to address the issues, or give you context for situations in which productivity was abnormally low. For example, severe weather conditions affecting the workers’ ability to come into the office or for a facility to operate normally, need to be accounted for in your data analysis so that you can determine what productivity factors you actually control and can improve on.
Step 8: Automate data collection and analysis
In order for productivity management analysis to help you measure and increase labor productivity, you need a program that doesn’t add to your organization’s work burden. Collecting data and analyzing the information can be difficult and tedious, which is why you may want to consider automated tools such as ActivTrak’s productivity management software and dashboards. Using automation can help you compile the data and analyze it quickly, so you can understand where your organization’s productivity stands and what steps to take to improve performance.
How do you measure work productivity in a remote team?
Measuring work productivity with a remote or hybrid team isn’t about watching every minute—it’s about understanding how work gets done. Here are some important considerations you’ll want to keep in mind:
- Focus on Results, Not Just Hours: It’s about what gets done, not how long someone is online.
- Leverage the Right Tools: Platforms like ActivTrak help identify work patterns and productivity trends.
- Set Clear Expectations: Define goals and KPIs early so employees know what success looks like.
- Check Collaboration & Engagement: Look at how your teams interact and contribute, not just individual output.
- Respect Work-Life Balance: Productivity thrives when employees feel trusted, not micromanaged.
By measuring work productivity the right way, businesses can ensure remote and hybrid teams stay aligned engaged, and efficient. The next step is taking action and turning your calculations into a plan for improvement.
Create an action plan to improve work productivity
Knowing how to measure work productivity is a great starting point for improving performance within your organization, but the insights are only valuable if you know how to act on them.
One way to do this is to create an action plan including steps you need to complete in order to reach your desired productivity level and any goals that will contribute to it. This plan has to be realistic and achievable in order to see increased productivity.
ActivTrak features several solutions to help you track and improve productivity, from labor hours to employee sentiment and more. Learn about our productivity management solutions, or contact us for more information.