Learn how to calculate productivity with this step-by-step guide including different productivity formulas and methods.
Productivity is a vital aspect of any successful business. It determines how well your organization produces goods or services, and is frequently tied to revenue and profits.
But how do you know if your workforce is as productive as possible? This is one area you don’t want to leave to chance. Measuring productivity — and knowing how to calculate it — is crucial for evaluating performance and identifying opportunities for improvement.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through a step-by-step process on how to calculate productivity, with valuable insights and actionable strategies along the way. Ready to get started? Let’s dive in.
What is productivity in business?
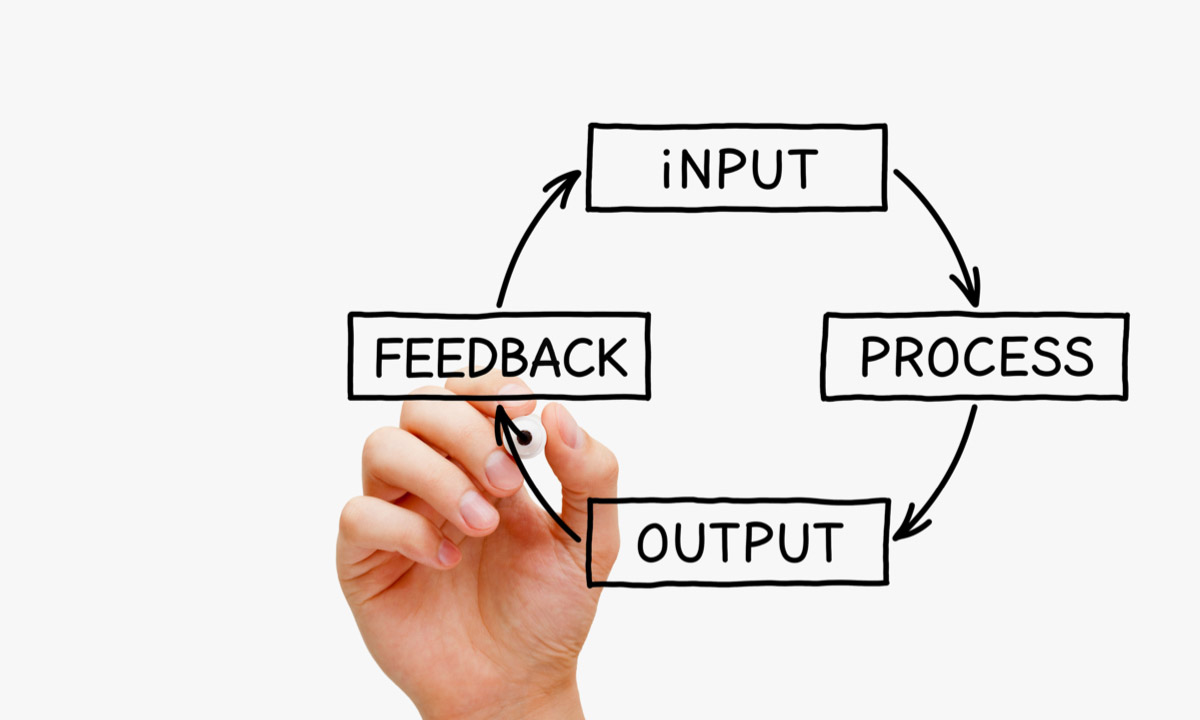
Productivity is a measure of business performance that tells you how efficiently employees achieve outputs based on inputs. Successful organizations regularly measure productivity to assess performance of individual employees, teams and the company as a whole — and to gauge both the quantity and quality of work.
Why should you calculate productivity?
Whether you’re a business leader, manager or employee, learning how to calculate productivity helps you make more informed decisions. Understanding employee productivity allows you to identify each person’s strengths and weaknesses — opening the door to personalized coaching and development opportunities designed to help individual employees thrive in their roles.
Measuring productivity also provides insight into the efficiency of business processes and reveals areas for improvement, like bottlenecks or unnecessary steps that can be refined to increase output.
The productivity formula
The best way to calculate productivity? Start with a basic formula to quantify the relationship between inputs and outputs:
Total Output / Total Input = Productivity
While the exact equation may vary depending on context, the general principle remains the same: Divide output (what your organization produced) by input (what your workforce did, or which resources were used, to achieve that output).
Components of the productivity formula
Here’s what each component means when you’re calculating productivity:
1. Output: This refers to the goods or services generated, such as the number of products produced or the amount of sales revenue generated.
2. Input: These are aspects that directly influence outputs, such as the amount of time spent on tasks or resources dedicated to a project.
3. Productivity: This tells you how efficiently and effectively your workforce is delivering results over a set period.
Common misconceptions about the productivity formula
To accurately calculate productivity levels, it’s important to avoid several common misconceptions. First, don’t make the mistake of focusing on the quantity of output without also factoring in quality. For example, working toward a productivity target based solely on the number of products produced may cause employees to take shortcuts. In this scenario, the rush may result in defective items. If the products are low quality and likely to be returned by customers, the quantity won’t matter — and your calculations won’t reflect true productivity.
Second, don’t overlook the importance of context. Productivity measurements vary widely across industries and sectors, so it’s critical to consider industry benchmarks and contextual data. When in doubt, use productivity management software to reduce your risk of erroneous conclusions due to inaccurate or missing data.
Considerations for calculating productivity
There are different ways to calculate productivity, both for your organization at large and for each team and employee. When determining the best way to measure productivity for each scenario, factor in several important considerations:
Industries and departments
In sectors with tangible outputs, such as manufacturing and retail, the number of units produced or sold can be an effective part of the productivity formula. But in the tech and service industries, you may need to focus on more nuanced metrics such as the number of milestones reached or critical tasks completed. Be prepared to tweak values by department, as well. While measuring productivity based on leads or deals closed would make sense for your sales team, marketing will need a different metric such as the percentage of goals achieved.
Benchmarks and goals
Are you in an established industry with clear benchmarks for productivity? If so, measure against those targets. These are especially important to factor in when calculating concrete outputs such as the number of customer service calls answered or support tickets resolved. Otherwise, set your own organizational benchmarks based on internal data.
Quality
To accurately calculate productivity, you need to factor in quality. Without including quality in productivity assessments, you won’t know if outputs are maintaining acceptable standards. To measure quality of work, create standards based on accuracy and functionality — and regularly check them as part of a quality assurance program for all outputs.
The 6 best ways to calculate productivity
There are several different ways to calculating productivity, you have several options depending on what metrics you have to work with.
1. The standard productivity formula
For some industries and departments, it may be easiest to use the productivity formula in its simplest form. Simply divide the number of goods or services produced by the total number of hours worked during a set period.
For example, let’s say it took 1,500 hours of labor for your workforce to produce 15,000 units last quarter.
- Output: 15,000 units
- Input: 1,500 hours of labor
Productivity: 15,000/1,500 = 10 units per hour
The standard productivity formula can tell you how effectively you’re utilizing inputs to create outputs, but it’s limited to a single factor — which is why it’s also called the partial factor productivity formula. While it works well for straightforward productivity calculations, you may need another method for a complete view.
2. Multifactor productivity
Multifactor productivity uses several inputs like labor, capital, and materials to provide a more comprehensive measure of productivity. Instead of dividing the output by a single input, you divide it by the sum of inputs for a holistic view.
For example, consider a scenario where you produced 8,000 units but required $2,000 in labor, $1,000 in capital, and $3,000 in materials.
- Output: 8,000 units
- Labor: $2,000
- Capital: $1,000
- Materials: $3,000
Multifactor productivity: 8,000/(2,000+1,000+3,000) = 1.33 units per dollar
Multifactor productivity is a more complex calculation, but provides insight on how each input affects the overall output. When multifactor productivity is lower than desired, you can look at which inputs require balancing or reduction.
3. Percentage of goal met
Calculating productivity as a percentage of goal met allows you to track progress toward a target or compare actual performance against the original goal. To use this method, divide the results by your original goal to get the percentage of goal met.
For example, let’s say you set a goal for your IT help desk to resolve 100 tickets each week and they exceed that to address 120.
- Result: 120 resolved tickets
- Goal: 100 resolved tickets
Percentage of goals met: 120/100 = 120% of goal
This method works well for teams that have clearly defined goals, along with target dates for achieving them. By using the goals-based method regularly — ideally monthly or quarterly — you can talk to employees about productivity in a way that’s focused on supporting them.
4. 360-degree feedback
With the 360-degree method, you collect feedback directly from employees and ask team members to rate how their peers have contributed to the success of the company. Then quantify feedback by using numerical ratings as scores for each person’s productivity.
For example, if you ask 10 employees to rate their peers’ productivity on a score of 1-5 in a survey or meeting, each person would have a minimum score of 9 (9 peers x scores of 1) and a maximum score of 45 (9 peers x scores of 5). If an employee receives a cumulative score of 40 from their peers, it indicates they’re perceived as highly productive.
However, it’s important to note that this data may be skewed based on personal preferences or limited knowledge about how others work. Employees may give high marks to friends, or may not work with some people frequently enough to understand their work habits.
5. Labor productivity
With this method, you can measure productivity as an average among employees within a team or the company as a whole. The labor productivity formula is simple — just divide the output generated over a specific period by the total number of employees working during that time.
For example, say you have 200 employees and you produced 1 million units over the last year.
- Output: 1,000,000 units produced in a year
- Number of Employees: 200
Labor productivity: 1,000,000/200 = 5,000 units per employee
You can also replace output with revenue to measure the average revenue each employee contributes relative to the total. The downside is that this method doesn’t give you a sense of each person’s productivity, which means you can’t identify employees who are performing above or below expectations.
6. Productivity management software
Productivity management software is ideal for companies that need a high degree of accuracy. These tools automatically collect employee activity data and weigh several factors to provide the most accurate measure of employee productivity. They show exactly how productivity changes over time and which factors are influencing it, at both the individual and team level. The software also reveals how, when, and where people are most productive so you can maximize performance.
If you’re looking for a quick, easy way to start calculating productivity at your company, ActivTrak’s Productivity Management Software is a great place to start. Request a demo to learn how you can begin generating detailed productivity reports today.
This article was originally published on Dec 26, 2023, then updated on May 15, 2025